Signature Verification
TEL re-validates Exhibit signatures whenever they are displayed, using the icon to indicate a successful re-validation (and using to indicate failed re-validation).
Successful revalidation confirms that the data has not changed since it was signed, and that it was signed by the user indicated.
Signature data may alternatively be re-validated yourself, using the procedure described here.
Requirements:
- Python 3.6 or better
- Python
rsapackage. On most systems, this may be installed with the commandpip install rsaafter installing python. - Live signature data from TEL. This can be obtained by visiting a public export link to a locker that includes one or more signed Exhibits.
Example
Here is an example Exhibit to validate:
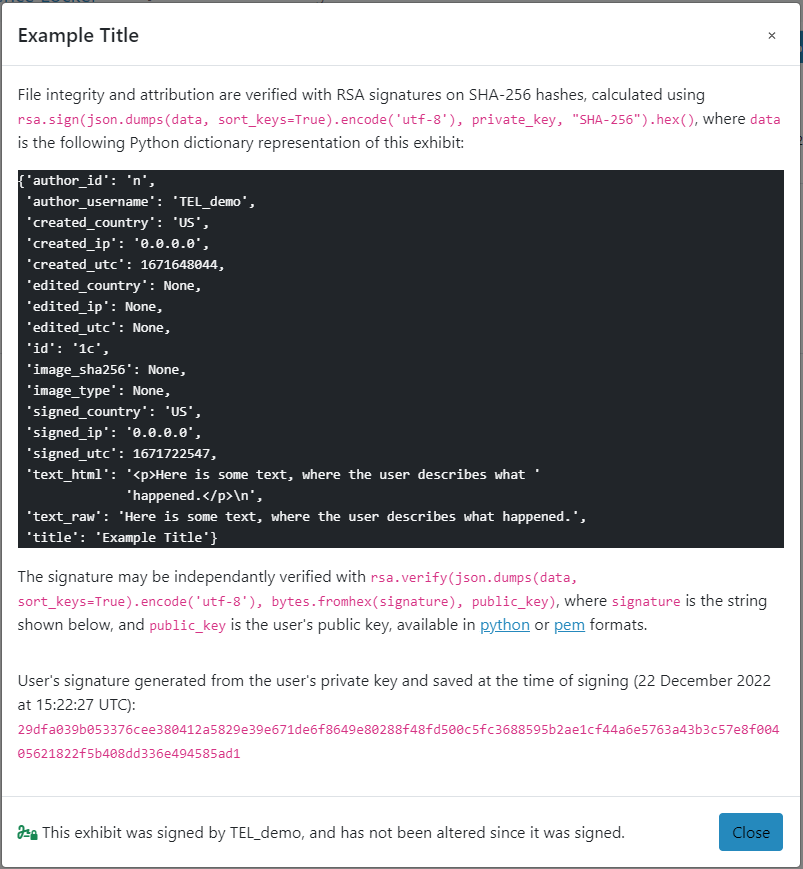
And here is its associated signature data:
The signature can be verified using IDLE, the default Python shell:
>>> # import rsa and json libraries
>>> import rsa
>>> import json
>>>
>>> # copy raw Exhibit data from TEL into a variable
>>> data = {'author_id': 'n',
'author_username': 'TEL_demo',
'created_country': 'US',
'created_ip': '0.0.0.0',
'created_utc': 1671648044,
'edited_country': None,
'edited_ip': None,
'edited_utc': None,
'id': '1c',
'image_sha256': None,
'image_type': None,
'signed_country': 'US',
'signed_ip': '0.0.0.0',
'signed_utc': 1671648044,
'text_html': '<p>Here is some text, where the user describes what '
'happened.</p>\n',
'text_raw': 'Here is some text, where the user describes what happened.',
'title': 'Example Title'}
>>>
>>> # copy signature string into a variable
>>> signature = "29dfa039b053376cee380412a5829e39e671de6f8649e80288f48fd500c5fc3688595b2ae1cf44a6e5763a43b3c57e8f00405621822f5b408dd336e494585ad1"
>>>
>>> # copy user's Python-formatted public key into a variable
>>> public_key = rsa.PublicKey(8555647050898027273016535636036195731439808637554611207272396463285836447566466728987015903224537133895221714709519944149942082827993524870192992289146397, 65537)
>>>
>>> # Verify signature. Expected output is the name of the hash function used to fingerprint the exhibit data.
>>> # Anything else, like an error, means verification failed.
>>> rsa.verify(json.dumps(data, sort_keys=True).encode('utf-8'), bytes.fromhex(signature), public_key)
'SHA-256'